This is important for financial reporting and decision-making because it takes into account both variable and fixed production costs. The salaries and benefits of supervisors and managers overseeing the production process are classified as fixed manufacturing overhead. The absorbed cost is a part of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), and is required when it comes to reporting your company’s financial statements to outside parties, including income tax reporting.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Absorption Costing
These materials were downloaded from PwC’s Viewpoint (viewpoint.pwc.com) under license. Charlene Rhinehart is a CPA , CFE, chair of an Illinois CPA Society committee, and has a degree in accounting and finance from DePaul University. Suppose XYZ Manufacturing produces 2,000 units of Widget X in a month. Deskera Books will assist in inventory management, automate inventory tracking and their insights. It also have backorder management which will ensure that you never fall short of any inventory.
Advantages of Absorption Costing
Knowing the full cost of producing each unit enables manufacturers to price their products. Under absorption costing, the inventory carries a portion of fixed overhead costs in its valuation. This means the cost of ending inventory on the balance sheet is higher compared to variable costing methods.
Absorption Costing vs. Variable Costing: An Accounting Perspective
However, ABC is a time-consuming and expensive system to implement and maintain, and so is not very cost-effective when all you want to do is allocate costs to be in accordance with GAAP or IFRS. In addition, the use of absorption costing generates a situation in which simply manufacturing more items that go unsold how puerto ricans are fighting back against using the island as a tax haven by the end of the period will increase net income. Because fixed costs are spread across all units manufactured, the unit fixed cost will decrease as more items are produced. Therefore, as production increases, net income naturally rises, because the fixed-cost portion of the cost of goods sold will decrease.
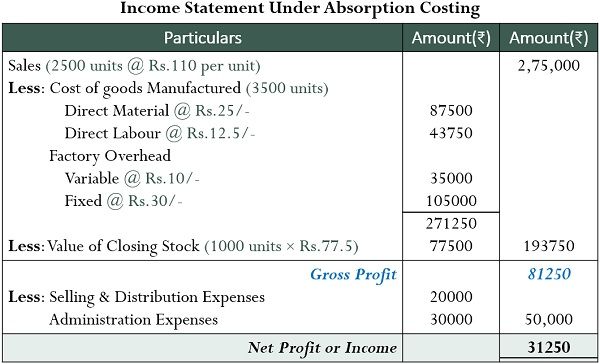
How do you calculate income statement under absorption costing?
This aids pricing strategies and gives an accurate inventory valuation. The tradeoff is that net profit fluctuates more than with variable costing methods. Understanding these basics helps explain the meaning and utility of absorption costing. Absorption costing is a method of costing that includes all manufacturing costs, both fixed and variable, in the cost of a product. Absorption costing is used to determine the cost of goods sold and ending inventory balances on the income statement and balance sheet, respectively. It is also used to calculate the profit margin on each unit of product and to determine the selling price of the product.
- Under generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), absorption costing is required for external financial reporting.
- After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career.
- The product of this calculation will indicate the amount of overhead to be applied (or charged) to production for the period.
- The percentage is obtained by dividing the overhead cost by the amount of direct labor.
Expenses incurred to ensure the quality of the products being manufactured, such as inspections and testing, are included in the absorption cost. These are expenses related to the manufacturing facility, and they are considered fixed costs. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental concept of absorption costing for accounting in manufacturing. Absorbed costs can include expenses like energy costs, equipment rental costs, insurance, leases, and property taxes. These expenses must have some tie-in to the manufacturing process or site, though—they can’t include advertising or administrative costs at corporate HQ. (f) Unsold stock-related fixed costs pass onto the next accounting period in part.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others. At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content. If a job involves direct wages of $1,000, the overhead to be absorbed amounts to $500 (i.e., 50% of $1,000).
Using these methods, overheads are recovered, charged to, or absorbed in the factory cost. The distribution of the accumulated overhead cost of a production department amongst its cost units is known as overhead absorption. This includes the cost of all materials that are directly used in the manufacturing process. These materials can be easily traced to a specific product, such as raw materials and components. It reveals inefficient or efficient production resource utilization by displaying under- or over-absorption of manufacturing overheads.
Absorption versus variable costing will only be a factor for companies that expense costs of goods sold (COGS) on their income statements. Any company can use both methods for various reasons but public companies are required to use absorption costing due to their GAAP accounting obligations. If overhead is over absorbed, this means that fewer actual overhead costs were incurred than expected, so that more cost is applied to cost objects than were actually incurred. This means that the recognition of expense is reduced in the current period, which increases profits. For example, if the overhead rate is predetermined to be $20 per direct labor hour consumed, but the actual amount should have been $18 per hour, then the $2 difference is considered to be over absorbed overhead.

